

- #Esp8266 firmware options how to#
- #Esp8266 firmware options install#
- #Esp8266 firmware options update#
- #Esp8266 firmware options download#
- #Esp8266 firmware options mac#
We can select the miscellaneous option for TLS/SSL support, debug as well.
#Esp8266 firmware options download#
String fwv = String(available_firmware_version) NodeMCU is an LUA based firmware which we need to download on the ESP8266 chip. Http.addHeader( "Content-Type", "application/x-String payload = http.getString() Http.begin( "") //Specify request destination const size_t capacity = JSON_OBJECT_SIZE( 2) + 60
#Esp8266 firmware options mac#
String mac = "mac_id=" + String(WiFi.macAddress()) # define firmware_version 1 // Initialise the DHT11 sensor. Your other sketch should have a different version number. # define DHTPIN 5 # define DHTTYPE DHT11 # define CSMS A0 // Set your firmware version here. The key name on the ESP8266 corresponds to the name argument in the HTML form on the web page. # include # include # include # include "DHT.h" // Set out Wifi auth constants. You can open the developer options in Chrome (F12) to check the HTTP request that are made when you click the button: youll see that it first send a POST request, and then receives a 303 (See Other) HTTP status as a response.
#Esp8266 firmware options update#
We check whether our firmware needs an update and update if necessary.Īnd finally we upload our binaries to the server, and make sure we have different version numbers for each build.We send our MAC address to the server which pings back the latest firmware version.


Now we build out our sketch and generate two different version numbers. Router.get( '/update', function( req, res, next) ) Var db = require( './js/databaseHandler') We’ll build a quick and dirty prototype where we connect all sensors to the ESP8266.
While they can be incredibly small, it’s pretty much impossible to reprogram them after soldering them to a PCB! Setting the scene I have found this a very useful thing to learn while I’ve been trying to reduce the size of my projects through the use of surface mounted ICs.
#Esp8266 firmware options how to#
ROM bootloader in the ESPĬhip uses this info to know how to talk to Image header along with the flash size andįlash frequency. Prepare a new firmware image file for writing. See esp32 and esp8266 for more information. board (Required, string): The board that should be used. Read the given section from currently opened Platform options that have been moved (now in platform-specific sections esp32 and esp8266): platform (Required, string): The type of platform. I recommend to change in nfig file flashmode to qio if your ESP module supports it and flash frequency to 40MHz if your module doesnt support 80MHz. The flashing command of AT2 with esptool is esptool.py writeflash nfig.
#Esp8266 firmware options install#
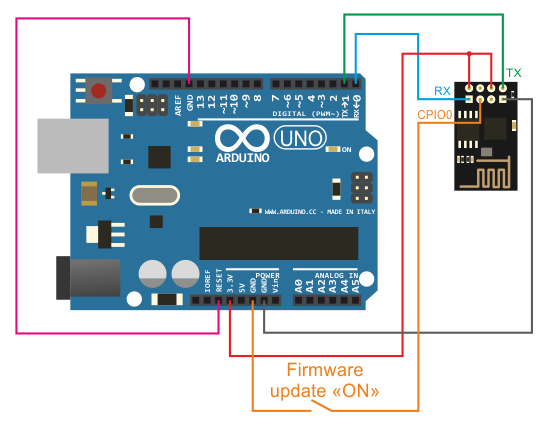
Open an ELF object file, parse it and cache AT firmware 2.1.x is build on Espressif RTOS SDK for esp8266 and esp32. ESP8266 Flash Downloader This method of flashing the ESP8266 to install the latest nodeMCU firmware uses the latest tool - which is also very easy to use, however you need to go and get a binary file for it to program into the chip - not too difficult.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
